We are exposed to many environmental and physical forces that tend to work against our well-being and health. Human body is equipped with a powerful protective system that protects the biological system from myriad of viruses, bacteria, toxins and parasites. These agents get inside our body and disturb the physiology of body leading to different types of disorders that can prove fatal in the absence of interventions. This protective shield is termed as immune system of the body.
What Is Included in the Immune System?
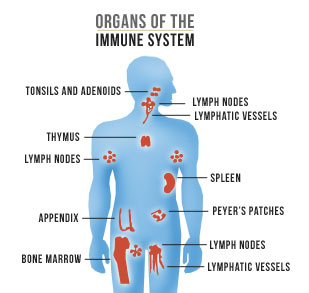
The Immune system has a number of functional components that help fight the foreign invaders in order to keep our body safe and secure. The immunological processes are carried out with the help of a variety of organs, tissues and cells, mainly white blood cells also known as leucocytes. But broadly speaking, these immune system components are vital for its functions.
Major Components of Immune System
|
Components |
Description |
|
Lymph nodes |
These are tiny kidney shaped structures that are responsible for storage and production of cells like antigens and antibodies in order to combat foreign invaders and neutralize their harmful effects. Lymph node contains fluid or lymph. This fluid helps the cells to move in body easily. While protecting the body from invaders lymph nodes increase in size in order to accommodate and produce larger number of cells for more rapid action. |
|
Spleen |
It is the most important and biggest lymphatic tissue of the body. It is located under your ribs on the left side of the body wall. It holds vital function in immunity as it possesses WBC’s (White Blood Cells). These cells are highly specialized in performing their function in the maintenance of immunity. Spleen is also regarded as dump-box for worn out blood cells to maintain the quantity as well as quality of blood cells in the circulation. |
|
Bone Marrow |
Bones contain two regions - the central marrow zone and the peripheral compact bone. The center portion contains spongy bone that accommodates yellow-colored marrow (or stem cells) which is responsible for the production of White blood cells as well as other cells. These stem cells can be transformed into any type of cell. This quality enhances the capability of immunity. |
|
Lymphocytes |
Lymphocytes have an essential role in the immunity; these are minute white blood cells and classified as:
|
|
Thymus |
This little organ is the place where T-cells earn their maturity. It also maintains the release of antibodies in body. At birth thymus is small; however, as the age proceeds it starts to grow but the pace of growth halts as puberty approaches. After puberty, this gland regresses due to fat deposition. |
|
Leukocytes |
Leukocytes comprise of different types of cells such as Macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, mast cells. These work in collaboration with each other and fight against the pathogens to keep the body safe. They are first to reach the site of infection and are mature enough to carry out their functions immediately. |
What Is the Function of the Immune System?
The most important function of immune system is to defend the body from different disease causing pathogens. Whenever there is pathology in human body, immune system is activated to protect the vital tissues from harm. Immune system has a remarkable capacity to differentiate between the physiological state of body and pathological state of body. This ability is attained with the help of two mechanisms:
- First mechanism is DAMPs Danger-associated Molecular Patterns. This mechanism detects the cell damage caused by cancer and sunburn because these are non-infectious agents.
- Second mechanism is termed as PAMPs Pathogen-associated Molecular Patterns. This mechanism sense and recognize the problems caused by infectious agents such as different bacteria and viruses.
When there is an infection in body, the immune system is automatically switched on so that it can come to the affected area and perform these functions but if due to any problem, the immune system is not activated, you can develop the symptoms of disease and illness.Likewise if immune is activated properly but due to some reasons it cannot be shut down, it can leave a negative impact on the body such as autoimmune diseases or allergic reactions.
Immune system is very unique and is very wide. Different types of cells from different part of body work in cooperation to perform the function of immunity. In short, immune system has all the capabilities starting from detecting the type of disease to fighting with it until it is eliminated from body.
What Disorders Would Occur If Immune System Is Not Working Well?
Immune system has a wide role in the body. If it over-reacts or under-performs, the risk of certain health issues increases:
1. Immunodeficiency Disorders
Immunodeficiency disorders are caused due to abnormal or inadequate functioning of the immune system. There are several types of immunodeficiency conditions:
- AIDS: This syndrome is the result of infection with HIV virus. This virus gets inside body and attack on the vital components of immune system; thereby affecting the quality of immune function. Once it succeeds in doing so, it takes charge of body and cause harm to body.
- Severe combined immunodeficiency disorder: This occurs in children as their immune system is weak and so they are more prone to different diseases.
2. Overactive Immune System
There are specific genes in body that usually become over-reactive and illicit uncontrolled immune responses to harmless stimuli. These proteins or stimuli are referred as allergens and may include pollen, dust or animal fur. Examples are:
- Asthma: Exposure to allergens evokes an allergenic response that affects the normal functioning of airways. This is characterized by sneezing and coughing.
- Eczema: Appearance of red spots or rashes on skin on exposure to allergens.
3. Autoimmune Disease
This type of disease causes the immune system to attack the healthy, functional cells of body. Examples are:
- Lupus: This disease affects the kidneys and lungs, leading to multi-organ dysfunction.
- Type 1 diabetes: Insulin is a hormone responsible to maintain the glucose levels of the blood. Autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic cells that are responsible for the secretion of insulin leads to diabetes type 1.
Here is a video to explain immune system in detail:
