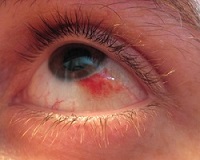
 Subconjuctival hemorrhage or bleeding behind eyes is typically painless and can be caused by a variety of medical conditions. Subconjuctival hemorrhage is commonly associated with high blood pressure, smoking, trauma to the eye or ingesting excessive amounts of salt or food additives. Learn about different causes of bleeding behind eyes, when you should worry as well as treatments and preventions for each condition.
Subconjuctival hemorrhage or bleeding behind eyes is typically painless and can be caused by a variety of medical conditions. Subconjuctival hemorrhage is commonly associated with high blood pressure, smoking, trauma to the eye or ingesting excessive amounts of salt or food additives. Learn about different causes of bleeding behind eyes, when you should worry as well as treatments and preventions for each condition.
Causes and Treatments of Bleeding Behind the Eye
1. Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
Definition
Subconjunctival hemorrhages are caused when blood vessels underneath the clear surface of the eye known as the conjunctiva break. The conjunctiva is not capable of absorbing blood quickly, so redness from the blood can become trapped here for some time. Many do not realize this has occurred until they see their reflection and note that their eye is bright red. This condition is often harmless, lasting for 10-14 days without additional harm to the eye.
Symptoms
Those suffering from a subconjunctival hemorrhage will note a red patch on the whites of their eye. This should not cause any pain or alter the vision in any way, though some may experience a scratchy sensation on the surface of the eye.
Causes
In most cases the cause of a subconjunctival hemorrhage is unknown, but some actions including powerful sneezing, violent coughing, vomiting or heavy lifting can cause the vessels in this area to break. Injuries to the eye such as surgery, severe infection or rubbing the eyes in a rough manner can also cause subconjunctival hemorrhage to occur.
Risk factors
Those that are using blood thinning medications like aspirin or warfarin, have an illness that causes severe sneezing or coughing, use herbal supplements like ginkgo or have high blood pressure and diabetes are at a higher risk for developing subconjunctival hemorrhage.
Treatments and Prevention
Unless you can identify the cause of the bleeding there is no way to prevent subconjunctival hemorrhage. Ceasing the use of blood thinning medications may help to relieve these symptoms. Those already experiencing subconjunctival hemorrhages can use eye drops if a scratchy sensation on the eye persists. The blood should absorb into the eye in 10-14 days, requiring no further treatment.
2. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy causes damage to the blood vessels in the eyes. As these blood vessels become weaker they become more susceptible to damage, which can lead to bleeding behind the eyes.
|
Description |
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes which causes damage to the retina and blood vessels in the eye. Those with type I and type II diabetes are at risk for developing this condition, though those that fail to properly control their blood pressure are at a higher risk for developing diabetic retinopathy. This condition will begin with mild vision problems, but can cause blindness if left untreated. As diabetic retinopathy sets in it may begin to cause blurred vision, dark strings or spots in the vision, empty or dark areas in the vision, fluctuating vision, difficulty with color perception or vision loss. These side effects can affect both eyes. |
|
Treatments |
Those with early diabetic retinopathy may not require treatment but will need to work with a doctor to monitor your condition. Working with an endocrinologist to improve the management of your diabetes can prevent these symptoms from becoming worse. Those that develop advanced diabetic retinopathy may need surgical treatment to correct retinal issues that stem from this condition.
|
|
Prevention |
|
3. Glaucoma
Glaucoma puts additional pressure on the eye, which will in turn put pressure on the blood vessels. As this condition worsens those that suffer from glaucoma will have an increased risk for seeing bleeding in the eye.
|
Description |
Glaucoma refers to a group of conditions that causes damage to the optic nerve, leading to damage to the vision. High pressure in the eye is commonly a cause of this damage. The loss of vision caused by glaucoma is gradual so many do not notice they are suffering from this condition until it is more advanced. Those suffering from glaucoma will frequently experience tunnel vision or a gradual loss of peripheral vision. As the condition becomes more acute they may notice eye pain, sudden onset of visual disturbances, nausea and vomiting, reddening of the eyes (bleeding behind eyes) or halos around lights. |
|
Treatments |
|
|
Prevention |
|
4. High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure causes damage to the blood vessels around the retina, increasing the risk that they will break and cause bleeding behind the eyes or in eyes. This is known as hypertensive retinopathy, a condition which can be serious if left untreated.
|
Description |
High blood pressure causes damage to blood vessels throughout the body, and the delicate blood vessels in the eyes are quite susceptible to damage from this condition. Those that are suffering from hypersensitive retinopathy will often experience vision problems and headaches, though the condition is typically diagnosed during a routine eye exam. |
|
Treatments |
In order to manage and eliminate the effects of hypertensive retinopathy, one must take steps with their doctor to control their blood pressure. |
|
Prevention |
Changes to your diet, increasing the amount of exercise you get each week and taking prescribed blood pressure medications as instructed can help to prevent hypertensive retinopathy. See your doctor regularly to ensure any necessary follow-up care is begun as quickly as possible. |
