A tendon is a strong, fibrous structure that joins muscle to bone, and tendinitis is irritation, inflammation, and swelling of that tendon. An inflamed tendonis usually the result of repetitive impact on the affected area. A sudden injury can also cause tendinitis, but the condition is more common in people over the age of 40 because tendons cannot tolerate serious stress as they age.
What Is Tendonitis?
A tendon may swell if you put pressure consistently through a repetitive motion. The inflammation of a tendon is called tendonitis and it causes serious pain and tenderness around the joint. Tendonitis can occur in different tendons in your body, but the condition usually affects tendons around your elbows, shoulders, knees, wrists, and heels. It is worth mentioning that some physicians may refer to tendonitis as golfer's elbow, tennis elbow, pitcher's shoulder, jumper's knee, and swimmer's shoulder. You can treat tendonitis with physical therapy, painkillers, and rest. Sometimes, tendonitis is severe and may tear a tendon completely. This condition requires surgery.
What Are the Symptoms of Tendonitis?
Tendonitis will often cause severe pain in the tissues surrounding the affected joint. The joint may lose strength and you may notice redness and swelling around the area. Sometimes, tendonitis can be the result of an infection like gonorrhea. If that is the case, the symptoms may include fever, rash, or discharges from the penis or vagina. Other common symptoms vary depending on which tendon is influenced:
- If it is rotator cuff tendonitis, the symptoms may includeaching, dull shoulder pain that moves into the upper arm to the chest. The pain becomes intolerable at night.
- You may notice pain occurred in the outer side of your elbow if you're the victim of a condition called tennis elbow. The pain may even go down to the wrist and forearm.
- Severe pain occurred in the inner side of your elbow may be a sign of golfer's elbow.
- Pain occurred below the kneecap is the outcome of jumper's knee.
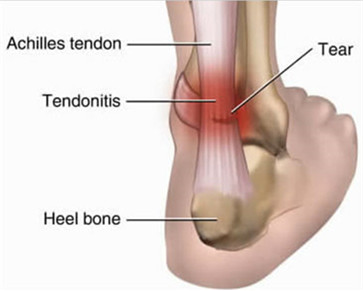
- Achilles tendonitis is usually the problem when you experience severe pain occurred at the back of your heel.
When to See a Doctor
In most cases, tendonitis responds well to self-care measures, but you should go see the doctor if the symptoms persist, interfere with your day-to-day activities, and keep you awake all night.
What Are the Causes & Risk Factors of Tendonitis?
After the common question, "what is tendonitis"?The next common question is about what leads to this situation. If you've been working on a computer for years, typing long lists of names or entering data, you are more likely to become a victim of tendonitis. It is therefore important to maintain a proper technique while performing repetitive job-activities or sports movements. Improper movements and techniques will overload the tendon and result in tendonitis.
Risk Factors
A risk factor is basically a situation or an activity that may increase the chances of developing a condition. Here are a few things that raise the risk of developing tendonitis.
|
Risk Factors |
Description |
|
Age |
As you get old, your tendons will become less flexible and you will be more susceptible to injuries and tendonitis. |
|
Specific Jobs |
If you're doing a job that requires repetitive movements, overhead stretching, awkward positions, or forceful exertion, your risk of developing tendonitis is higher. |
|
Sports |
Certain sports that involve repetitive movements such as tennis, basketball, swimming, golf, baseball, bowling, and running may increase the risk of developing tendonitis. |
|
Diabetes |
Though it's not clear yet, you may be more susceptible to developing tendonitis if you have diabetes. |
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
People with rheumatoid arthritis may develop a condition called tenosynovitis in which the sheath surrounding the tendon gets inflamed. |
What Are the Treatments for Tendonitis?
The basic goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain:
- Rest or immobilization of the affected tendons usually helps a lot with recovery. You may consider using a removable brace or a splint to immobilize a tendon. The application of heat or cold packs may also help reduce inflammation.
- Non-Steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can also play a role in reducing pain and inflammation. Sometimes, your doctor may administer steroids injections into the tendon sheath to control pain. Remember, you may require physical therapy, but it is important to make pain manageable first to start physical therapy.
- The use of specific physical therapy techniques that may strengthen and stretch the tendon and muscle also proves beneficial in most cases. Physical therapy may also help restore your tendon's ability to function properly – this also improves healing and prevents future injury. A shockwave therapy is usually recommended when there are calcium deposits around the tendon.
- Surgery is a treatment option in some cases when the injury is severe. The surgery usually involves removing the inflammatory tissue to eliminate pain.
How to Prevent Tendonitis
Once you know the answer to the question, "What is tendonitis?"you should get educated about how to prevent it from happening. You can take some specific steps to reduce the chances of developing tendonitis. For instance:
- Exercise regularly and use weight training to build your muscle tone
- Never overlook the importance of warming up before exercising
- Avoid or limit repetitive and overuse motions
- Always cross-train when you're an athlete
- Learn and maintain proper posture when working at a desk
- Invest in proper equipment while working or during athletic activities
